What Is GTM Engineering? Key Principles, Roles, and Comparisons Explained (2025)
What Is GTM Engineering? Key Principles, Roles, and Comparisons Explained (2025)
Estimated reading time: 14 minutes
Key Takeaways
GTM engineering merges technology, business, and revenue operations to enable faster, more scalable growth.
It focuses on measurable revenue impact, automation, and cross-functional collaboration rather than purely technical outputs.
GTM engineering principles include automation, integration, data-driven optimization, personalization at scale, and end-to-end visibility.
The GTM engineer role requires both technical expertise and business acumen, bridging product, marketing, sales, and revenue teams.
Adopting GTM engineering improves efficiency, accelerates product launches, and delivers a strong competitive edge.
Table of contents
What Is GTM Engineering? Key Principles, Roles, and Comparisons Explained (2025)
What Is GTM Engineering? (Definition, Meaning, and Full Form)
GTM engineering is a specialized discipline at the intersection of technology, business, and revenue operations. In this blog, we’ll explore its meaning, core principles, roles, and how it compares to traditional methods, offering a comprehensive guide on its benefits, challenges, and future trends.
What Is GTM Engineering? (Definition, Meaning, and Full Form)
GTM engineering is a specialized discipline that designs, automates, and optimizes the technical systems driving a company's go-to-market strategies. It integrates tools and data pipelines to support rapid product launches, lead routing, marketing automation, sales outreach, and analytics for sustainable revenue growth.
At its core, GTM engineering ensures all systems work together seamlessly: from capturing and enriching data to personalizing outreach and measuring impact. Unlike traditional engineering, it focuses on revenue impact and launch speed.
GTM full form in engineering: “Go-To-Market.” GTM engineering executes and optimizes go-to-market strategies with a primary lens on business outcomes.
For more detail, seeCandyboxCRM’s resource,GTM Alliance’s guide,FullEnrich,Persana AI,andSalesforge.
Overview of GTM Engineering
“GTM engineering evolved from siloed revenue operations.” As organizations expanded, sales, marketing, and revenue ops often developed distinct tools and strategies. This led to disconnected data sources, manual processes, and limited visibility.
GTM engineering emerged to solve this by unifying the tech stack, orchestrating end-to-end customer journeys, and delivering automation that respects SLAs. Modern GTM engineers work with CRM platforms like Salesforce or HubSpot, marketing automation (Marketo, HubSpot), data warehouses (Snowflake, BigQuery), and more.
A typical reference architecture includes:
Ingest: Capture data from forms, product telemetry, ads
Normalize/Enrich: Improve data quality, add firmographics
Route: Implement lead/account ownership logic
Orchestrate: Create workflows for SLAs and outreach
Activate: Launch personalized campaigns
Measure: Build dashboards and perform cohort analysis
Govern: Conduct audits and enforce data contracts
For more background, refer to marketing technology stack overview and FullEnrich’s blog.
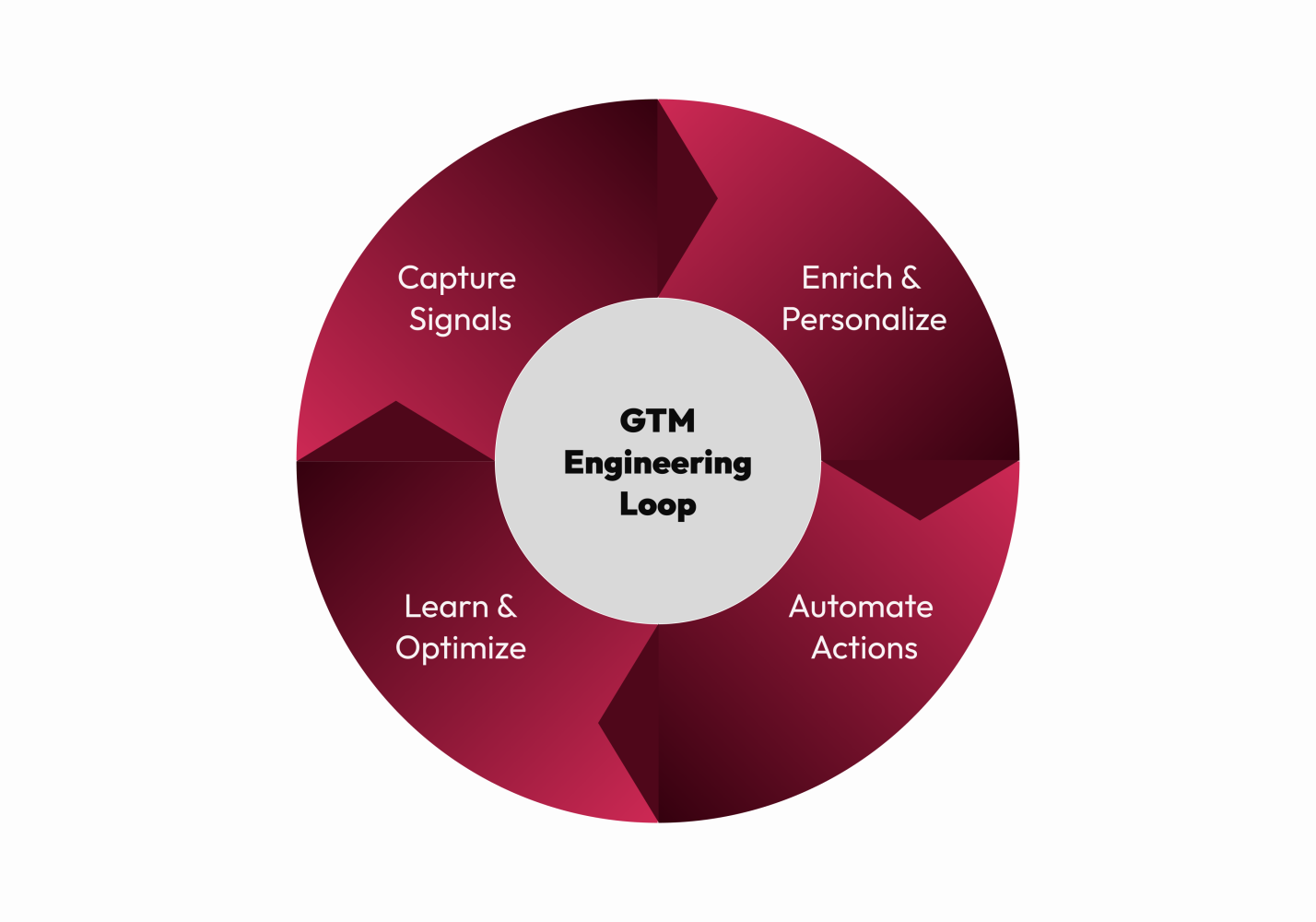
Key Principles of GTM Engineering
GTM engineering is distinguished by five core principles:
Automation: Replace manual steps with auditable workflows (lead scoring, routing, follow-ups)
Integration: Reliably connect systems with bidirectional data flows and robust error handling
Data-driven Optimization: Build pipelines and analytics for enrichment, segmentation, and performance measurement
Personalization at Scale: Use AI and dynamic logic to craft tailored messaging without human overhead
End-to-End Visibility: Instrument every stage of the funnel, from awareness to retention
Unlike other engineering disciplines, GTM engineering prioritizes revenue impact over strict coding standards, remaining agile to market changes. For further reading, see CandyboxCRM’s blog and GTM Alliance.
GTM Engineering vs. Traditional Engineering Methods
While both GTM engineering and traditional engineering require technical proficiency, they diverge in core focus and metrics of success. Traditional engineers typically measure uptime, latency, and code quality, while GTM engineers track pipeline velocity, revenue, and launch speed.
Core Focus:
• GTM Engineering: Automating revenue processes, measuring marketing and sales impact, orchestrating cross-functional workflows
• Traditional Engineering: Building product features, ensuring system reliability, maintaining infrastructure
Success Metrics:
• GTM Engineering: Pipeline velocity, operational efficiency, revenue growth
• Traditional Engineering: Uptime, defect rates, performance benchmarks
Consider Google’s GTM approach, which aligns technical systems and business stakeholders for over 100 monthly feature launches. It’s a prime example of how GTM engineering can accelerate market readiness.
Roles and Responsibilities in GTM Engineering
What is a GTM engineer? They’re hybrid professionals combining technical expertise (APIs, data pipelines) with business acumen (funnel metrics, segmentation). They bridge product, marketing, sales, and revenue operations to deliver automated, data-driven processes.
Core Responsibilities:
Architect data models and integrations (contacts, leads, accounts, opportunities)
Build and maintain automations (lead scoring, routing, MQL/SQL transitions)
Enforce data integrity (deduplication, normalization, governance)
Orchestrate CRM, marketing automation, enrichment, and sales engagement platforms
Develop dashboards and reports for funnel analysis and revenue attribution
How does this differ from software engineering? GTM engineers are revenue-focused, business-facing, and toolchain-oriented rather than purely coding new features or systems.
A typical day might include diagnosing lead routing errors, updating dashboards, collaborating on launch workflows, and scaling product-qualified lead triggers.See FullEnrich, Salesforge, and GTM Alliance for further insights.
Benefits of Adopting GTM Engineering
Organizations leveraging GTM engineering can realize:
Increased Efficiency: Reduced manual tasks, quicker lead response times, fewer errors
More Innovation and Strategic Focus: Freed up time to focus on creativity, better campaign development, and higher-level planning
Transformational Business Impact: Faster launches, improved funnel conversion, better alignment, and deeper customer satisfaction
Common improvements include shorter sales cycles, improved stage-to-stage conversion, and reduced operational tickets. For instance, lead response times can drop by 70% or more. CandyboxCRM and GTM Alliance highlight these benefits in depth.
Challenges and the Future of GTM Engineering
Common Challenges:
• Tool fragmentation with unmaintained integrations• Data quality issues (duplicates, conflicting schemas)• Talent scarcity for hybrid technical-business roles
Future Outlook:
• AI-Driven Orchestration: Automating lead scoring, routing, and personalization• No-Code/Low-Code Maturity: Empowering broader teams to build simpler automations• Ecosystem-Level Integrations: Streamlined connectors that reduce custom code• Revenue Intelligence Platforms: Deeper buyer behavior and sales analytics
Governance considerations like change management, audit trails, data privacy, and permissioning will also grow in importance. For more, see GTM Alliance and FullEnrich.
90-Day GTM Engineering Implementation Playbook
For companies looking to adopt or strengthen GTM engineering, this phased approach is effective:
Phase 1 (Days 1-30): Discovery and Stabilization
Map current data flows and SLAs, implement monitoring, fix priority sync failures, define data contracts, identify quick wins.Phase 2 (Days 31-60): Automate and Integrate
Deploy lead routing/scoring, unify lifecycle stage definitions, build core dashboards, standardize lead qualification, set up basic nurture flows.Phase 3 (Days 61-90): Personalize and Scale
Integrate product telemetry for product-qualified leads, implement AI-assisted sales outreach, document governance, deploy advanced analytics, review system performance regularly.
Connecting these phases back to the core principles of automation, integration, data-driven optimization, personalization, and visibility ensures tangible results at each step. See CandyboxCRM,GTM Alliance,FullEnrich, and Persana AI for more details.
Conclusion
GTM engineering is a pivotal evolution in executing go-to-market strategies. By focusing on revenue, speed, and cross-functional alignment, teams can deliver measurable outcomes that bridge product, marketing, sales, and revenue ops.
As AI, analytics, and no-code platforms mature, GTM engineering becomes increasingly strategic—shortening sales cycles, personalizing outreach at scale, and continuously informing teams on what truly drives growth. For professionals, it’s a dynamic, in-demand career path; for organizations, it’s a competitive advantage in today’s fast-evolving markets.
Frequently Asked Questions
GTM explained: What is GTM Engineering in one sentence?
GTM Engineering is the design and automation of the systems powering go-to-market strategy to drive efficient, scalable revenue growth.
What is the GTM full form in engineering?
GTM stands for Go-To-Market.
What is a GTM engineer?
A GTM engineer is a hybrid technologist who engineers solutions for go-to-market systems, automations, and data flows to achieve growth and operational efficiency.
How does GTM Engineering differ from traditional engineering?
GTM Engineering emphasizes revenue impact, cross-functional collaboration, and rapid adaptability over purely technical indicators like performance or code quality.
Is GTM Engineering relevant beyond tech companies?
Yes. Any organization seeking fast, data-driven, and customer-centric go-to-market execution can use GTM engineering principles, regardless of industry.

